Time:2025-08-25 15:54:57 Number of Clicks:
Belt conveyor systems are the "arteries" for material transportation in fields such as mining, ports, power plants, and chemical industries. Their operational stability is directly related to the efficiency and safety of the entire production line. However, conveyor belts are highly susceptible to faults like deviation, slipping, tearing, and overload during operation—minor issues may cause shutdowns and production halts, while severe ones can lead to significant equipment damage or even safety accidents. Therefore, a complete and reliable safety protection system is not only a "compliance requirement" but also an "essential measure" to ensure personal safety and economic benefits.
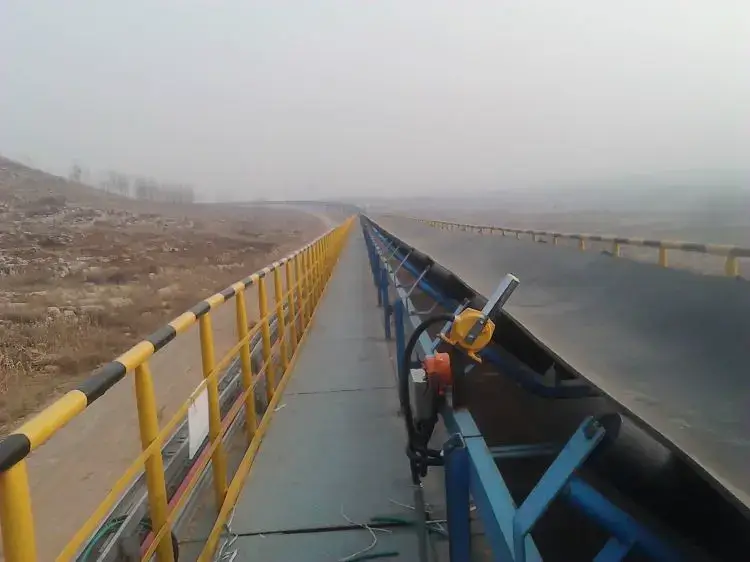

Belt deviation is the most common fault, which can cause wear, material spillage, and even jamming and shutdown.
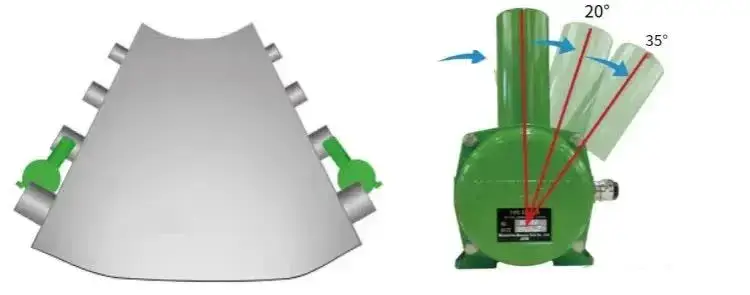
Slip indicates insufficient friction between the drive drum and the belt, which can cause wear, high temperatures, and even fire.
Belt slip detection devices can real-time monitor the actual operating speed of the belt and compare it with the theoretical speed (usually derived from the drive drum speed). When the speed difference exceeds the set threshold (e.g., 70%-85% of the rated speed), an alarm or shutdown signal is sent.
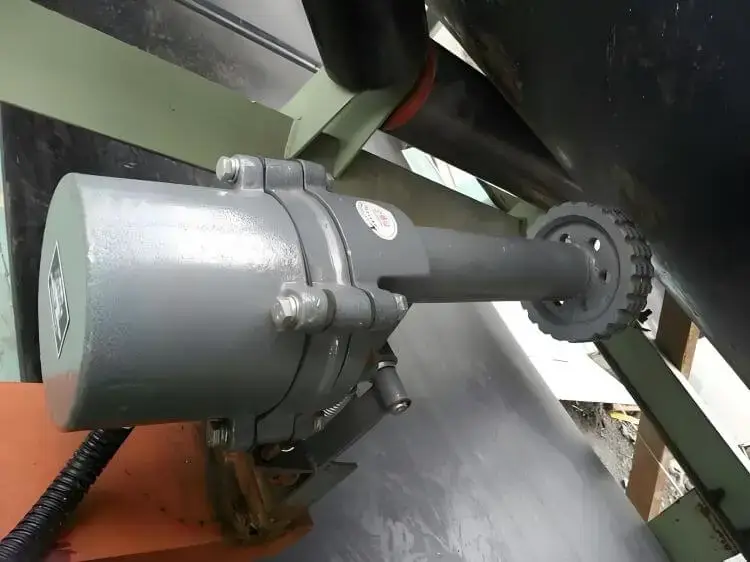

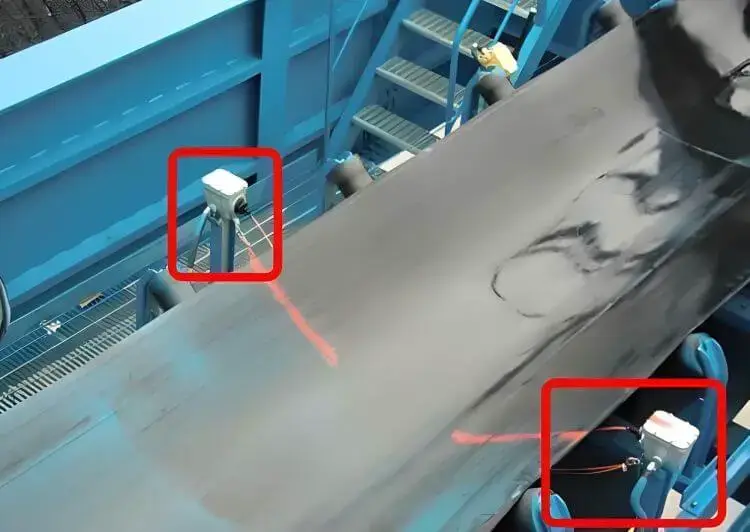
Longitudinal belt tearing is a catastrophic fault with extremely high repair costs.
Belt tear detection devices can quickly detect tearing at an early stage and trigger an emergency shutdown to prevent the tear from expanding.
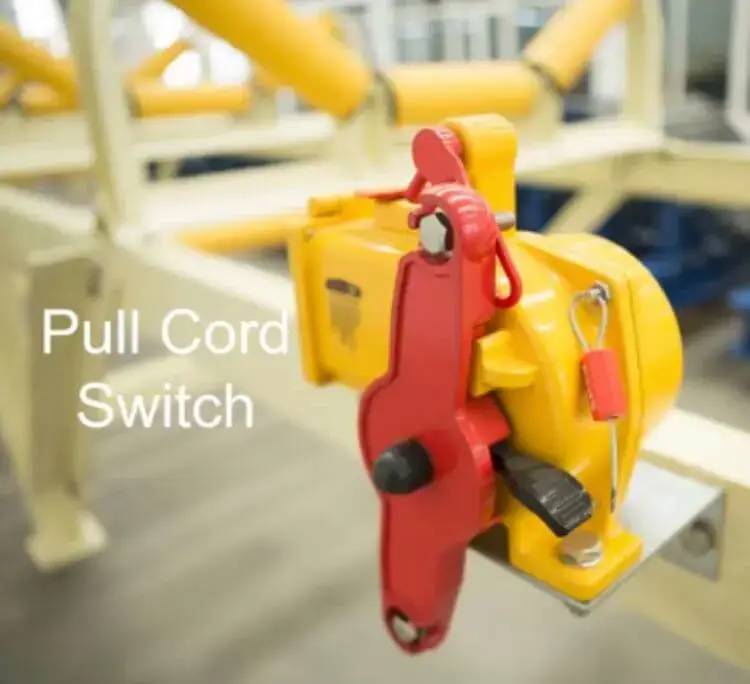
In case of an emergency at any position along the line, personnel can manually trigger the device to stop the conveyor immediately.
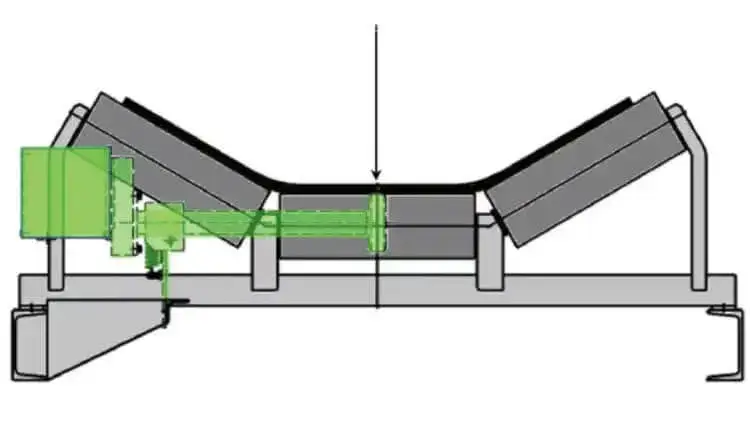
Overload protection devices can prevent the motor from being burned due to overload or the belt from being damaged due to excessive tension.
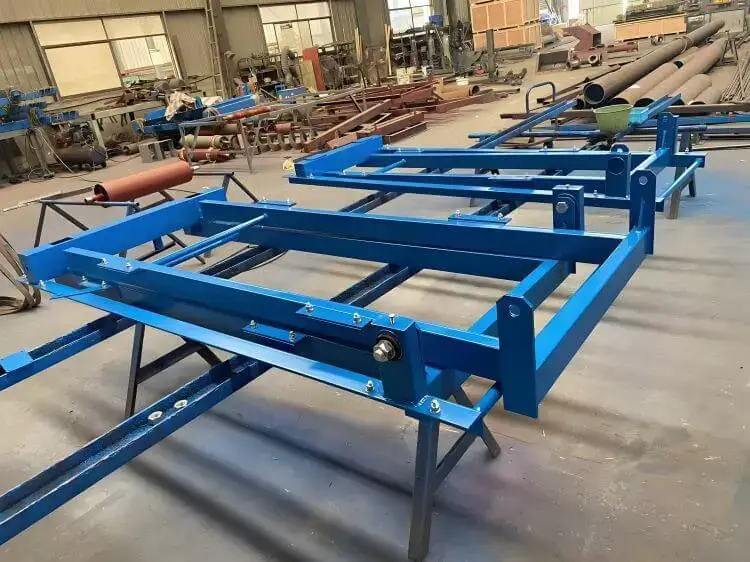

Anti-reversal protection devices can prevent the upward-conveying belt from reversing due to the gravity of materials after shutdown, which may cause material accumulation, belt blockage, and damage.

Temperature and smoke monitoring devices can monitor abnormal temperatures at key parts and early fire smoke to prevent fire.
In addition to slip protection, it also includes:
Limit the travel range of heavy-duty components such as tensioning trolleys and mobile tails to prevent mechanical collisions caused by exceeding the limit position.
Characteristics: Adopt heavy-duty limit switches with high protection class (IP67), resistance to vibration and impact, and the output signal is directly connected to the safety circuit.
Provide stable power for belt protection devices, sensors, and lighting in remote areas without external power supply (such as mine mining areas).
Characteristics: Usually adopt the method of kinetic energy recovery (obtaining power from belt operation) + storage battery to ensure the safety system works uninterruptedly under any circumstances.
An effective safety protection system is not just a simple combination of equipment; it also requires reasonable selection, correct installation, and regular maintenance.
| Type of Protection Device | Common Specific Types | Core Function | Structure / Operating Characteristics | Typical Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Belt Deviation Protection Device | ① Two-Stage Deviation Switch ② Automatic Deviation Correction Device (Self-Aligning Idler, Hydraulic Deviation Corrector) | ① Monitor the deviation amplitude of the belt from the center line; issue first-level deviation alarm and second-level deviation shutdown (to avoid belt wear / material spillage); ② Automatically correct belt deviation without shutdown. | ① Mechanical contact type / photoelectric type, installed on both sides of the belt (10-30cm from the center line), response time ≤ 0.5s; ② Mechanical structure (self-aligning idler) or hydraulic drive, passive / active correction, no electrical failure risk. | All conveyor belts (especially long-distance and wide belts) |
| 2. Belt Slip Protection Device | ① Speed Sensor (Magnetoelectric / Photoelectric Type) ② Slip Detector (Linked with Drum) | Monitor the actual operating speed of the belt; when the speed is lower than the set value (e.g., 70%-80% of the rated speed), issue an alarm and shut down (to prevent overheating, fire, and material accumulation caused by friction between the belt and the drum). | ① Non-contact (photoelectric) or contact (magnetoelectric) type, synchronous speed measurement with the belt / drum, accuracy ±0.5%; ② Directly installed on the driven drum, mechanical triggering, strong resistance to dust interference. | High-load belts (e.g., coal conveying belts in mines and power plants) |
| 3. Belt Tear Protection Device | ① Contact Type (Steel Cable Type, Plate Type) ② Non-Contact Type (Ultrasonic / Infrared Type) | Detect whether the belt has longitudinal tearing (e.g., belt scratched by sharp impurities in materials); shut down immediately (to prevent tear expansion and belt scrapping). | ① Contact type: Triggered by the steel cable / plate when the belt is torn, high mechanical reliability but requiring contact with the belt; ② Non-contact type: Scan the belt integrity through ultrasonic waves, no wear, suitable for high-dust / humid environments. | Belts conveying ores, construction waste, and other materials with sharp impurities |
| 4. Emergency Shutdown Protection Device | ① Pull Rope Switch (Along-the-Line Arrangement) ② Emergency Stop Button (Key Positions) ③ Emergency Pull Cable | In emergency situations (e.g., personnel straying into the area, equipment jamming), manually cut off the power to shut down the belt (serving as the final safety line); ③ Trigger shutdown by pulling the steel cable, covering belts in complex terrains. | ① Pull rope switch: One switch installed every 30-50m along the entire length of the belt, triggered by pulling the rope, covering the entire stroke; ② Emergency stop button: Installed in the operation room and at the head / tail of the belt, push-type, instant response; ③ Steel cable material (tensile strength ≥500N), with anti-corrosion shell, suitable for belts in complex paths such as curves and slopes. | ①② All conveyor belts (mandatory standard configuration); ③ Field and complex terrain belts (e.g., mountain belts in mines) |
| 5. Overload Protection Device | ① Belt Scale (Flow Monitoring) ② Tension Sensor ③ Motor Overload Protector | Prevent the belt from bearing more than the design load: ① Monitor material flow and alarm when exceeding the limit; ② Monitor belt tension and shut down when overloaded; ③ Monitor motor current and cut off power when overloaded. | ① Belt scale: Installed under the belt, dynamic weighing, can link with the feeder to adjust the flow; ② Tension sensor: Installed on the tensioning device, real-time tension feedback; ③ Electrical protection, low cost and easy maintenance. | Bulk cargo (coal, ore) conveying belts in ports |
| 6. Anti-Reversal Protection Device | ① Ratchet Backstop ② Belt-Type Backstop ③ Hydraulic Backstop | Prevent reversed rotation of inclined belts (inclination angle >15°) after shutdown (to avoid material backflow and belt stacking damage to equipment). | ① Mechanical structure (ratchet + pawl), no power dependency, reliability >99%; ② Belt-type: Braking through friction between the brake belt and the drum, suitable for medium and low-speed belts; ③ Hydraulic drive, stable braking, suitable for high-speed / heavy-load belts. | Inclined belts (e.g., underground and hoisting belts in mines) |
| 7. Temperature and Smoke Protection Device | ① Temperature Sensor (Drum / Bearing) ② Smoke Sensor | Prevent fire caused by friction: ① Monitor the temperature of the drum / bearing, alarm and shut down when overheated (e.g., >80℃); ② Detect smoke generated by friction and provide early fire warning. | ① Contact-type temperature probe (high-temperature-resistant material), installed on the drum end cover; ② Photoelectric smoke sensor, high sensitivity, can link with fire extinguishing devices. | High-speed and long-distance belts (e.g., coal conveying belts in power plants, chemical belts) |
| 8. Material Blockage Protection Device | ① Blockage Switch (Rotary / Capacitive Type) ② Level Sensor | Detect material blockage at hoppers and chutes (to avoid belt overload / deviation caused by accumulated materials); alarm and shut down when blocked. | ① Rotary type: The blade stops rotating when blocked by materials, triggering the switch; ② Capacitive type: Detect through the change of material dielectric constant, non-contact, suitable for viscous materials. | Belts with hoppers / chutes (e.g., cement and grain conveying belts) |
| 9. Position Limit Protection Device | ① Heavy-Duty Limit Switch | Limit the extreme position of heavy-duty moving components in the belt system (e.g., tensioning frame, telescopic head); alarm and enforce shutdown when exceeding the stroke (to prevent structural collision and belt tearing). | Heavy-duty structure (able to withstand impact force ≥1000N), contact life ≥100,000 times, protection class IP65 (dustproof and waterproof), installed at the end of the component movement path, hard-linked with the belt control system (manual reset required after power-off). | ① Mobile frame of large counterweight tensioning device; ② Head / tail of telescopic belt conveyor; ③ Hydraulic adjustment mechanism of heavy-duty idler group. |
| 10. Auxiliary Power Supply Protection Device | ① On-Site Power Generation Device (Belt Kinetic Energy Driven) | Use the kinetic energy of the running belt (e.g., drum rotation) to drive a micro generator for power generation, providing continuous power for IoT sensors (e.g., deviation and temperature sensors), on-site lighting, and emergency equipment; solve the problem of no external power supply in remote areas. | Integrating a micro permanent magnet generator (power 5-50W), energy storage module (lithium battery / super capacitor), and voltage stabilization circuit, installed at the shaft end of the driven drum without affecting the normal operation of the belt, power generation efficiency ≥60%, suitable for belt speeds of 0.5-5m/s. | Field belts without external power supply (e.g., belts in remote mining areas, oilfield heat-tracing oil conveying belts), IoT monitoring belts |
Copyright © 2002-2024 Zoomry Group Company Limited